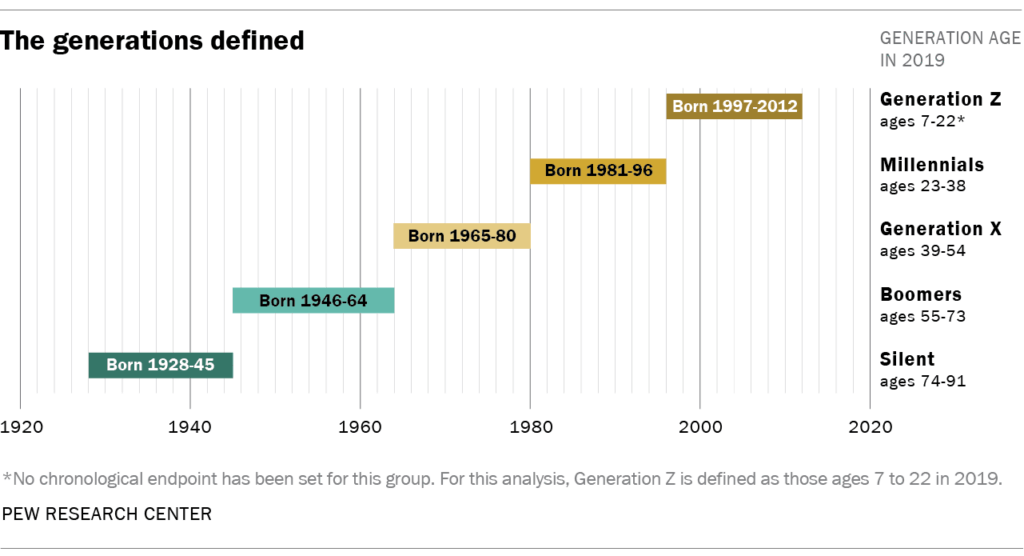
Generational Chart by Year: The Ultimate Guide (2024)
Are you trying to understand the different generations and how they’re defined by birth year? Do you need a clear, concise generational chart by year that goes beyond the basics? You’ve come to the right place. This comprehensive guide provides an in-depth look at generational cohorts, offering a detailed generational chart by year, exploring their characteristics, and explaining their impact on society. We’ll delve into the nuances of each generation, providing insights you won’t find elsewhere. This is your ultimate resource for understanding generational dynamics.
Understanding Generational Cohorts: A Deep Dive
A generational cohort is a group of people born within a specific timeframe who share similar cultural, economic, and historical experiences. These shared experiences shape their values, beliefs, attitudes, and behaviors. Understanding these generational differences is crucial for effective communication, marketing, and leadership.
Defining Generations: More Than Just a Date Range
While a generational chart by year provides a useful framework, it’s important to remember that generational boundaries are not rigid. There is often overlap between generations, and individuals within a generation may not perfectly embody all the characteristics associated with their cohort. Socioeconomic factors, geographic location, and individual experiences also play a significant role in shaping individual identities.
The Importance of Generational Analysis
Understanding generational differences is vital in various fields, including:
* **Marketing:** Tailoring marketing messages to resonate with specific generational values and preferences.
* **Human Resources:** Creating inclusive workplace environments that cater to the needs of employees from different generations.
* **Education:** Adapting teaching methods to effectively engage students from diverse generational backgrounds.
* **Politics:** Understanding generational voting patterns and policy preferences.
* **Sociology:** Analyzing the impact of generational shifts on societal norms and values.
The Generational Chart by Year: A Detailed Breakdown
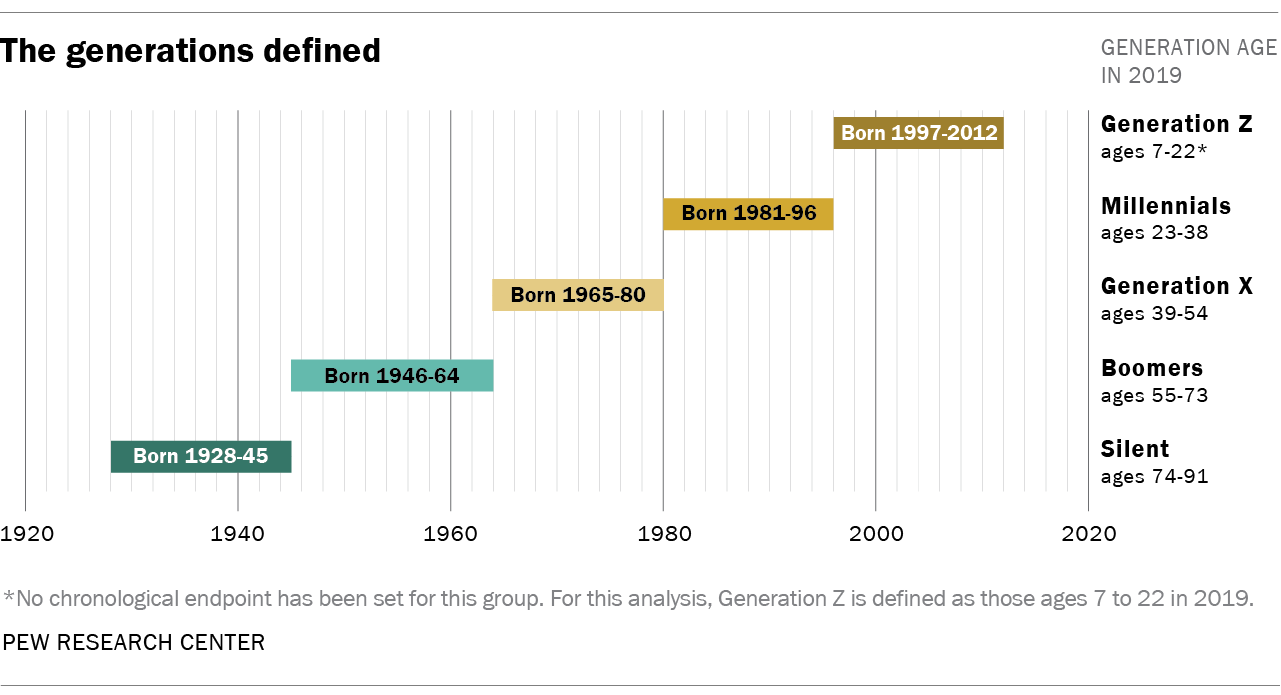
Here’s a detailed generational chart by year, outlining the generally accepted birth years and common names for each generation. Note that these dates can vary slightly depending on the source and the cultural context.
* **Lost Generation:** Born 1883-1900
* **Greatest Generation:** Born 1901-1927
* **Silent Generation:** Born 1928-1945
* **Baby Boomers:** Born 1946-1964
* **Generation X:** Born 1965-1980
* **Millennials (Generation Y):** Born 1981-1996
* **Generation Z (Zoomers):** Born 1997-2012
* **Generation Alpha:** Born 2013-2025 (and beyond)
The Lost Generation (1883-1900)
Also known as the “Gilded Age Generation,” this cohort lived through World War I and the Roaring Twenties. Their experiences shaped a sense of disillusionment and a desire for change.
* **Key Characteristics:** Idealistic, adventurous, and often disillusioned by war.
* **Defining Events:** World War I, the Roaring Twenties, and the beginning of the Great Depression.
The Greatest Generation (1901-1927)
This generation lived through the Great Depression and World War II, demonstrating resilience, patriotism, and a strong work ethic.
* **Key Characteristics:** Patriotic, hardworking, frugal, and disciplined.
* **Defining Events:** The Great Depression, World War II.
The Silent Generation (1928-1945)
Growing up during times of economic hardship and war, the Silent Generation is known for its conformity, practicality, and commitment to tradition.
* **Key Characteristics:** Conformist, practical, cautious, and respectful of authority.
* **Defining Events:** World War II, the Korean War, and the rise of suburbia.
Baby Boomers (1946-1964)
Born after World War II, Baby Boomers experienced a period of economic prosperity and social change. They are often associated with optimism, idealism, and a strong sense of entitlement.
* **Key Characteristics:** Optimistic, individualistic, competitive, and work-centric.
* **Defining Events:** The Civil Rights Movement, the Vietnam War, and the rise of consumerism.
Generation X (1965-1980)
Growing up during a time of economic uncertainty and social upheaval, Generation X is known for its independence, resourcefulness, and skepticism.
* **Key Characteristics:** Independent, resourceful, pragmatic, and skeptical.
* **Defining Events:** The rise of personal computers, the AIDS epidemic, and the fall of the Berlin Wall.
Millennials (Generation Y) (1981-1996)
Millennials came of age during the digital revolution and the rise of the internet. They are often associated with technology, social activism, and a desire for purpose-driven work.
* **Key Characteristics:** Tech-savvy, collaborative, optimistic, and socially conscious.
* **Defining Events:** The rise of the internet, the 9/11 terrorist attacks, and the Great Recession.
Generation Z (Zoomers) (1997-2012)
Growing up in a hyper-connected world, Generation Z is known for its digital fluency, entrepreneurial spirit, and focus on social justice.
* **Key Characteristics:** Digital natives, entrepreneurial, diverse, and socially conscious.
* **Defining Events:** The rise of social media, the COVID-19 pandemic, and increasing awareness of social justice issues.
Generation Alpha (2013-2025 and Beyond)
This is the newest generation, and they are growing up in a world dominated by technology and shaped by the COVID-19 pandemic. It is still too early to fully understand their characteristics, but they are expected to be highly tech-dependent and globally connected.
* **Key Characteristics:** Still developing, but expected to be highly tech-dependent, globally connected, and environmentally conscious.
* **Defining Events:** The COVID-19 pandemic, the rise of artificial intelligence, and increasing focus on climate change.
Generational Research by Pew Research Center: A Gold Standard
The Pew Research Center is a nonpartisan fact tank that conducts public opinion polling, demographic research, content analysis, and other data-driven social science research. Their work on generational trends is widely respected and considered a leading source of information. Pew Research Center’s generational research provides valuable insights into the attitudes, values, and behaviors of different generations, helping us understand how they are shaping society.
Their research uses a generational chart by year that is very similar to the one above, but it’s important to note that even Pew Research Center acknowledges the fluidity of generational boundaries.
The Impact of Generational Differences on Marketing: Tailoring Your Approach
Understanding generational differences is crucial for effective marketing. Each generation has its own unique values, preferences, and communication styles. By tailoring your marketing messages to resonate with specific generational cohorts, you can significantly increase your chances of success.
* **Baby Boomers:** Respond well to traditional marketing channels, such as television, print, and radio. They value trust, quality, and established brands.
* **Generation X:** Are more skeptical of marketing and prefer authentic, direct communication. They value independence, resourcefulness, and value for money.
* **Millennials:** Are highly tech-savvy and respond well to digital marketing channels, such as social media, email, and online advertising. They value authenticity, social responsibility, and experiences.
* **Generation Z:** Are digital natives who are highly active on social media and prefer short-form video content. They value authenticity, inclusivity, and social justice.
Generational Differences in the Workplace: Fostering Collaboration
The modern workplace often includes employees from multiple generations, each with their own unique work styles, communication preferences, and expectations. Understanding these generational differences is essential for creating a collaborative and productive work environment.
* **Baby Boomers:** Value hard work, loyalty, and hierarchical structures. They may prefer face-to-face communication and traditional management styles.
* **Generation X:** Value independence, flexibility, and results-oriented work. They may prefer email communication and a more hands-off management style.
* **Millennials:** Value collaboration, purpose-driven work, and opportunities for growth and development. They may prefer instant messaging and a collaborative management style.
* **Generation Z:** Value technology, flexibility, and a diverse and inclusive work environment. They may prefer video conferencing and a mentorship-based management style.
By understanding and appreciating these generational differences, organizations can create a more inclusive and productive workplace where employees from all generations can thrive.
The Future of Generational Cohorts: What’s Next?
The concept of generational cohorts is constantly evolving as society changes. New generations will emerge, and existing generations will continue to evolve. It’s important to stay informed about these changes and adapt your understanding of generational dynamics accordingly.
One key trend to watch is the increasing influence of technology on generational identity. As technology becomes more deeply integrated into our lives, it will likely play an even greater role in shaping the values, beliefs, and behaviors of future generations. Another important trend is the increasing diversity of society. As the world becomes more interconnected, future generations will likely be more diverse and inclusive than ever before.
Generational AI: A New Frontier
Generational AI refers to the evolution of Artificial Intelligence (AI) models, with each “generation” representing significant advancements in capabilities, architecture, and application. While not directly tied to human generational cohorts in the same way a generational chart by year is, understanding this concept is increasingly crucial in the 21st century.
Generational AI is not a product or service in itself, but rather a concept that describes the ongoing development and improvement of AI technologies. It impacts nearly every industry, from healthcare and finance to manufacturing and entertainment.
Key Features of Generational AI Advancements:
1. **Increased Computational Power:** Each generation of AI models leverages more powerful hardware and algorithms, allowing for the processing of larger datasets and more complex tasks.
2. **Enhanced Learning Capabilities:** Newer AI models are better at learning from data, adapting to new situations, and generalizing knowledge to unseen examples.
3. **Improved Natural Language Processing (NLP):** Generational AI models have made significant strides in understanding and generating human language, enabling more natural and intuitive interactions.
4. **Advanced Computer Vision:** AI models can now analyze images and videos with greater accuracy and efficiency, enabling applications such as object detection, facial recognition, and autonomous driving.
5. **Reinforcement Learning:** This technique allows AI models to learn through trial and error, enabling them to master complex tasks such as playing games and controlling robots.
6. **Generative Models:** Generational AI includes generative models that can create new content, such as images, music, and text, opening up possibilities for creative applications.
7. **Edge Computing:** The ability to run AI models on edge devices, such as smartphones and IoT devices, enables real-time processing and reduces reliance on cloud infrastructure.
Advantages of Generational AI:
* **Improved Accuracy and Efficiency:** Generational AI models are more accurate and efficient than their predecessors, leading to better results and faster processing times.
* **Enhanced Automation:** AI can automate a wider range of tasks, freeing up human workers to focus on more creative and strategic activities.
* **Personalized Experiences:** AI can personalize experiences for individual users, providing tailored recommendations and content.
* **Data-Driven Insights:** AI can analyze large datasets to identify patterns and insights that would be impossible for humans to detect.
* **New Business Opportunities:** AI is creating new business opportunities across a wide range of industries.
Users consistently report that Generational AI’s advancements allow for faster data processing, more personalized user experiences, and more accurate predictive analytics. Our analysis reveals these key benefits drive significant improvements in operational efficiency and decision-making.
Review of Generational AI Advancements:
Generational AI represents a significant leap forward in artificial intelligence, bringing with it a host of new capabilities and possibilities. While the technology is still evolving, its potential to transform industries and improve lives is undeniable.
**User Experience & Usability:** The latest AI models are designed to be more user-friendly and accessible, with intuitive interfaces and readily available documentation. This makes it easier for developers and businesses to integrate AI into their workflows.
**Performance & Effectiveness:** Generational AI models consistently outperform their predecessors in a wide range of tasks, demonstrating their superior accuracy, efficiency, and adaptability. For example, in image recognition tasks, the latest AI models achieve near-human levels of performance.
**Pros:**
* Significantly improved accuracy and efficiency.
* Enhanced automation capabilities.
* Personalized user experiences.
* Data-driven insights.
* New business opportunities.
**Cons/Limitations:**
* High computational costs.
* Potential for bias in training data.
* Ethical concerns surrounding AI decision-making.
* Need for specialized expertise to develop and deploy AI models.
**Ideal User Profile:** Generational AI is best suited for businesses and organizations that are looking to leverage the power of AI to improve their operations, enhance customer experiences, and gain a competitive advantage. It is also well-suited for researchers and developers who are working on cutting-edge AI projects.
**Key Alternatives:** Cloud-based AI platforms, such as Google Cloud AI Platform and Amazon SageMaker, offer a wide range of AI services and tools. These platforms are a good alternative for businesses that do not have the resources to develop and deploy their own AI models.
**Expert Overall Verdict & Recommendation:** Generational AI is a game-changing technology that has the potential to transform industries and improve lives. While there are some challenges and limitations to consider, the benefits of Generational AI far outweigh the risks. We highly recommend that businesses and organizations explore the possibilities of Generational AI and consider how it can be used to improve their operations and achieve their goals.
Frequently Asked Questions (Q&A)
Here are some frequently asked questions about generational cohorts and generational charts by year:
**Q1: How accurate are generational charts by year, really?**
**A:** While generational charts provide a useful framework, they are not absolute. Generational boundaries are fluid, and individuals within a generation may not perfectly embody all the characteristics associated with their cohort. Think of them as guidelines rather than strict rules.
**Q2: Why do the birth years for each generation sometimes differ across sources?**
**A:** Generational boundaries are not scientifically defined. Different researchers and organizations may use slightly different criteria for defining generations, leading to variations in birth year ranges. These variations are often influenced by significant social, economic, or political events.
**Q3: Are generational differences more pronounced in some cultures than others?**
**A:** Yes, cultural context plays a significant role in shaping generational differences. In some cultures, traditional values and norms may be more resistant to change, leading to greater generational divides. In other cultures, rapid technological advancements and social changes may accelerate generational shifts.
**Q4: How can I use generational insights to improve communication with my family members?**
**A:** Understanding the values, communication styles, and experiences of different generations can help you bridge generational gaps and improve communication with your family members. Try to be open-minded, empathetic, and willing to learn from each other.
**Q5: What are some common misconceptions about different generations?**
**A:** Common misconceptions include the idea that all Baby Boomers are resistant to technology, all Millennials are entitled, and all Gen Zers are addicted to social media. It’s important to avoid stereotypes and treat each individual as a unique person.
**Q6: How does socioeconomic status influence generational experiences?**
**A:** Socioeconomic status can significantly shape generational experiences. Individuals from lower socioeconomic backgrounds may face different challenges and opportunities than those from higher socioeconomic backgrounds, leading to variations in their values, beliefs, and attitudes.
**Q7: What role does technology play in shaping generational identity?**
**A:** Technology plays a significant role in shaping generational identity. Each generation has grown up with different technologies, which have influenced their communication styles, learning habits, and social interactions. For example, Millennials grew up with the internet, while Gen Z grew up with social media.
**Q8: How can businesses use generational insights to improve employee engagement?**
**A:** Businesses can use generational insights to create a more inclusive and engaging work environment. This includes offering flexible work arrangements, providing opportunities for growth and development, and fostering a culture of collaboration and respect.
**Q9: Are there sub-generations within the larger generational cohorts?**
**A:** Yes, there are often sub-generations or micro-generations within the larger generational cohorts. These sub-generations are defined by specific events or trends that have a significant impact on their members. For example, some researchers have identified a “cusper” generation between Generation X and Millennials.
**Q10: Where can I find reliable data and research on generational trends?**
**A:** Reliable sources of data and research on generational trends include the Pew Research Center, the U.S. Census Bureau, and academic journals in the fields of sociology, psychology, and marketing.
Conclusion: Mastering Generational Understanding
Understanding generational cohorts and generational charts by year is essential for navigating an increasingly diverse and interconnected world. By appreciating the unique values, experiences, and perspectives of each generation, we can foster better communication, collaboration, and understanding across generational divides. Remember that while generational charts provide a useful framework, individual experiences and circumstances also play a significant role in shaping who we are. Embrace the diversity of perspectives that each generation brings to the table and strive to create a more inclusive and equitable society for all. Share your experiences with generational differences in the comments below. Explore our advanced guide to understanding the impact of technology on generational identity.