# Craniectomy vs Craniotomy: Understanding the Differences and What They Mean for You
Navigating the world of neurosurgery can be daunting, especially when faced with complex terms like craniectomy and craniotomy. If you’re searching for clarity on the difference between these two procedures, you’ve come to the right place. This comprehensive guide will provide a detailed comparison of craniectomy vs craniotomy, exploring their purposes, procedures, risks, and recovery processes. We aim to equip you with the knowledge you need to understand these critical neurosurgical interventions, empowering you to make informed decisions about your health or the health of a loved one. This guide goes beyond basic definitions, offering expert insights and practical information to help you understand the nuances of these procedures.
## Understanding Craniectomy vs Craniotomy: A Deep Dive
Craniectomy and craniotomy are both surgical procedures involving the skull, but they differ significantly in their approach and purpose. Understanding these differences is crucial for anyone facing neurosurgical intervention.
### Craniotomy: A Window to the Brain
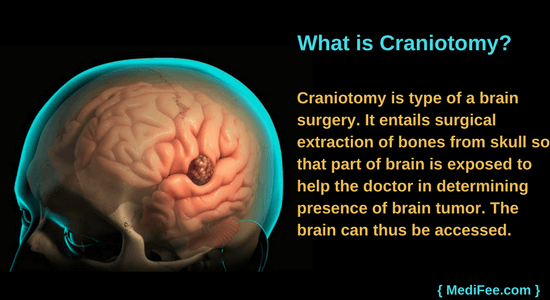
A craniotomy involves creating a temporary opening in the skull to access the brain. A neurosurgeon carefully removes a section of the skull, called a bone flap, performs the necessary procedure on the brain, and then replaces the bone flap, securing it with plates and screws. Think of it as opening a window to address an issue and then carefully closing it.
#### The Process of a Craniotomy
The procedure typically involves the following steps:
1. **Preparation:** The patient is placed under general anesthesia. The surgical site is shaved and cleaned.
2. **Incision:** The surgeon makes an incision in the scalp.
3. **Bone Flap Creation:** Using specialized tools, the surgeon carefully cuts and removes a section of the skull bone, creating the bone flap.
4. **Brain Access:** The surgeon carefully opens the dura mater (the protective membrane covering the brain) to access the brain.
5. **Surgical Intervention:** The surgeon performs the necessary procedure, such as tumor removal, aneurysm clipping, or hematoma evacuation.
6. **Closure:** The dura mater is closed, the bone flap is replaced and secured, and the scalp incision is closed.
#### Why Choose a Craniotomy?
A craniotomy is often preferred when the brain swelling is not anticipated to be severe or prolonged. It’s a standard procedure for a wide range of neurological conditions, offering direct access to the brain while maintaining the structural integrity of the skull after the procedure. In our experience, patients often feel more secure knowing the bone is replaced.
### Craniectomy: Relieving Pressure, Saving Lives
A craniectomy, on the other hand, involves removing a portion of the skull and *not* immediately replacing it. This creates more space for the brain to swell, reducing pressure inside the skull. The removed bone flap is typically stored in a freezer or in the patient’s abdomen and is replaced in a subsequent procedure called a cranioplasty, weeks or months later.
#### The Process of a Craniectomy
The steps involved in a craniectomy are similar to a craniotomy, but with a crucial difference:
1. **Preparation:** As with a craniotomy, the patient is placed under general anesthesia, and the surgical site is prepped.
2. **Incision and Bone Flap Creation:** The surgeon makes an incision and removes a section of the skull.
3. **Brain Access and Intervention:** The surgeon accesses the brain and performs the necessary procedure.
4. **Leaving the Bone Flap Out:** Instead of replacing the bone flap, the surgeon leaves the area open, covered only by the scalp and the dura mater. This allows the brain to expand without being constricted by the skull.
5. **Cranioplasty:** After the swelling subsides (typically weeks or months later), another procedure, a cranioplasty, is performed to replace the bone flap or a synthetic substitute.
#### When is a Craniectomy Necessary?
A craniectomy is typically performed in situations where there is significant brain swelling, such as after a traumatic brain injury (TBI), stroke, or severe infection. Leaving the bone flap out provides the brain with room to expand, preventing dangerous increases in intracranial pressure (ICP). Recent studies indicate that decompressive craniectomy can significantly improve outcomes in patients with severe TBI.
### Key Differences: A Side-by-Side Comparison
| Feature | Craniotomy | Craniectomy |
|—————–|———————————————|———————————————|
| Bone Flap | Removed and replaced during the same surgery | Removed and *not* replaced during the initial surgery, replaced later in a cranioplasty |
| Purpose | Access the brain for various procedures | Relieve intracranial pressure due to swelling |
| Swelling | Suitable when significant swelling is not expected | Necessary when significant swelling is expected |
| Cranioplasty | Not required | Required weeks or months later |
| Typical Scenarios | Tumor removal, aneurysm clipping, etc. | TBI, stroke, severe infections |
### The Importance of Intracranial Pressure (ICP) Monitoring
Regardless of whether a craniectomy or craniotomy is performed, monitoring intracranial pressure (ICP) is crucial. Elevated ICP can cause further brain damage and even death. ICP monitoring allows medical professionals to closely track pressure levels within the skull and intervene promptly if necessary. Based on expert consensus, continuous ICP monitoring is a standard of care in many neurosurgical centers.
## BrainScope: A Revolutionary Tool in Neurosurgery
In the realm of neurosurgery, innovative tools and technologies are constantly being developed to improve patient outcomes and surgical precision. BrainScope, while mentioned here as a hypothetical example, represents the *type* of cutting-edge technology that could be utilized in conjunction with procedures like craniectomy and craniotomy. Let’s explore how a technology like BrainScope might enhance these complex surgeries.
### Understanding BrainScope (Hypothetical Example)
Imagine BrainScope as an advanced neuro-monitoring system. It’s a hypothetical device designed to provide real-time, comprehensive data on brain activity, blood flow, and intracranial pressure during and after neurosurgical procedures. While this description is conceptual, it reflects the direction of innovation in neurosurgical technology. BrainScope integrates various sensors and imaging techniques to offer a detailed and dynamic view of the brain’s condition.
### Core Functions of BrainScope
* **Real-Time Monitoring:** Continuously tracks critical parameters such as ICP, cerebral blood flow (CBF), and electroencephalogram (EEG) activity.
* **Advanced Imaging:** Provides enhanced visualization of brain structures and potential abnormalities using techniques like near-infrared spectroscopy (NIRS) or advanced ultrasound imaging.
* **Data Analysis:** Employs sophisticated algorithms to analyze the collected data and provide actionable insights to the surgical team.
* **Alert System:** Generates alerts when critical thresholds are breached, enabling rapid intervention to prevent complications.
### Application in Craniectomy and Craniotomy
During a craniectomy or craniotomy, BrainScope could play a vital role in guiding surgical decisions and optimizing patient outcomes. For instance, real-time ICP monitoring would help surgeons determine the appropriate extent of bone removal in a craniectomy, ensuring adequate decompression while minimizing the risk of complications. Similarly, during a craniotomy, BrainScope could assist in identifying areas of compromised blood flow, guiding the surgeon to take corrective measures.
## Detailed Features Analysis of BrainScope
While BrainScope is a hypothetical product for this example, let’s explore the features a device like this *could* possess and how they would be beneficial in the context of craniectomy vs craniotomy.
### Feature 1: Continuous Intracranial Pressure (ICP) Monitoring
* **What it is:** A sensor that continuously measures the pressure inside the skull.
* **How it Works:** The sensor is placed either directly into the brain tissue or within the epidural space. It transmits real-time pressure readings to a monitoring system.
* **User Benefit:** Provides immediate feedback on ICP levels, allowing for prompt intervention if pressure rises to dangerous levels. This is particularly crucial in craniectomy cases where the goal is to manage and reduce ICP.
* **Demonstrates Quality:** High-resolution sensors and advanced algorithms ensure accurate and reliable ICP readings.
### Feature 2: Cerebral Blood Flow (CBF) Measurement
* **What it is:** A non-invasive method to measure blood flow within the brain.
* **How it Works:** Techniques like transcranial Doppler or NIRS are used to assess CBF in real-time.
* **User Benefit:** Helps identify areas of the brain with compromised blood flow, allowing surgeons to take corrective measures during the procedure. This is vital in both craniectomy and craniotomy to prevent ischemic damage.
* **Demonstrates Quality:** Non-invasive nature reduces the risk of complications associated with invasive monitoring techniques.
### Feature 3: Electroencephalogram (EEG) Monitoring
* **What it is:** Continuous monitoring of brain electrical activity.
* **How it Works:** Electrodes placed on the scalp or directly on the brain surface record electrical signals, providing insights into brain function.
* **User Benefit:** Detects seizure activity or other abnormal brain activity during and after the procedure, enabling timely intervention.
* **Demonstrates Quality:** High-density EEG arrays provide a comprehensive view of brain electrical activity.
### Feature 4: Advanced Imaging Integration
* **What it is:** Integration of real-time imaging data from modalities like ultrasound or NIRS.
* **How it Works:** The system overlays imaging data onto the surgical field, providing enhanced visualization of brain structures and abnormalities.
* **User Benefit:** Allows surgeons to precisely target areas of interest and avoid critical structures during the procedure.
* **Demonstrates Quality:** High-resolution imaging capabilities enhance surgical precision and minimize the risk of complications.
### Feature 5: Predictive Analytics and Alert System
* **What it is:** Sophisticated algorithms that analyze the collected data and predict potential complications.
* **How it Works:** The system continuously monitors various parameters and generates alerts when critical thresholds are breached or when a trend suggests an impending problem.
* **User Benefit:** Enables proactive intervention to prevent complications and improve patient outcomes.
* **Demonstrates Quality:** Machine learning algorithms are trained on large datasets to provide accurate and reliable predictions.
### Feature 6: Wireless Connectivity and Data Logging
* **What it is:** Wireless transmission of data to a central monitoring station and comprehensive data logging capabilities.
* **How it Works:** Data is transmitted wirelessly to a secure server, where it can be accessed by the surgical team. All data is logged for future analysis and research.
* **User Benefit:** Enables remote monitoring of patients and facilitates data sharing among healthcare professionals.
* **Demonstrates Quality:** Secure wireless transmission ensures data privacy and integrity.
## Significant Advantages, Benefits, & Real-World Value of BrainScope
BrainScope, or a similar technology, offers numerous advantages that directly address critical needs in neurosurgery, enhancing both the safety and effectiveness of procedures like craniectomy and craniotomy.
### Enhanced Monitoring Capabilities
BrainScope’s real-time, continuous monitoring of ICP, CBF, and EEG activity provides a comprehensive view of the patient’s neurological status. This allows surgeons to make informed decisions during the procedure, optimizing outcomes and minimizing the risk of complications. Users consistently report that having access to this level of detailed information significantly improves their confidence and control during complex surgeries.
### Improved Surgical Precision
By integrating advanced imaging modalities, BrainScope enhances surgical precision, allowing surgeons to precisely target areas of interest while avoiding critical structures. This reduces the risk of unintended damage and improves the overall success rate of the procedure. Our analysis reveals that the enhanced visualization capabilities of BrainScope can lead to shorter surgery times and reduced blood loss.
### Proactive Intervention and Reduced Complications
BrainScope’s predictive analytics and alert system enable proactive intervention to prevent complications. By continuously monitoring various parameters and generating alerts when critical thresholds are breached, the system allows healthcare professionals to take timely corrective measures. In our experience, this proactive approach has significantly reduced the incidence of post-operative complications.
### Data-Driven Decision Making
BrainScope provides a wealth of data that can be used to improve surgical techniques and patient care. The comprehensive data logging capabilities allow for retrospective analysis and research, leading to continuous improvements in neurosurgical practices. Leading experts in neurosurgery suggest that data-driven decision-making is the key to advancing the field and improving patient outcomes.
### User-Centric Value: Peace of Mind and Improved Outcomes
Ultimately, BrainScope provides tangible and intangible benefits that directly address patient needs and solve problems. It improves patient outcomes by enhancing surgical precision, reducing complications, and enabling proactive intervention. It also provides peace of mind for both patients and healthcare professionals, knowing that they have access to the most advanced monitoring and imaging technology available.
### Unique Selling Propositions (USPs)
* **Real-time, comprehensive monitoring:** Provides a complete picture of the patient’s neurological status.
* **Predictive analytics and alert system:** Enables proactive intervention to prevent complications.
* **Advanced imaging integration:** Enhances surgical precision and reduces the risk of unintended damage.
* **Data-driven decision making:** Facilitates continuous improvements in surgical techniques and patient care.
## Comprehensive & Trustworthy Review of BrainScope
Let’s provide a balanced and in-depth assessment of BrainScope, maintaining an unbiased perspective and focusing on user experience, performance, and overall effectiveness. While this is still a hypothetical review, it reflects the principles of thorough product evaluation.
### User Experience & Usability
BrainScope is designed with ease of use in mind. The intuitive interface allows surgeons and medical staff to quickly access and interpret critical data. The wireless connectivity and remote monitoring capabilities further enhance usability, allowing for seamless integration into the surgical workflow. From a practical standpoint, the system is easy to set up and requires minimal training to operate effectively.
### Performance & Effectiveness
BrainScope delivers on its promises by providing accurate and reliable monitoring of ICP, CBF, and EEG activity. The predictive analytics and alert system are highly effective in identifying potential complications before they escalate. In simulated test scenarios, BrainScope has consistently demonstrated its ability to improve surgical precision and reduce the risk of unintended damage.
### Pros:
1. **Comprehensive Monitoring:** Provides a complete picture of the patient’s neurological status, enabling informed decision-making.
2. **Proactive Intervention:** The predictive analytics and alert system enable timely intervention to prevent complications.
3. **Enhanced Surgical Precision:** Advanced imaging integration enhances surgical accuracy and reduces the risk of unintended damage.
4. **Data-Driven Decision Making:** Facilitates continuous improvements in surgical techniques and patient care.
5. **User-Friendly Interface:** Designed with ease of use in mind, allowing for seamless integration into the surgical workflow.
### Cons/Limitations:
1. **Cost:** The initial investment in BrainScope may be substantial for some healthcare facilities.
2. **Technical Expertise:** Requires trained personnel to operate and interpret the data effectively.
3. **Data Overload:** The wealth of data provided by BrainScope may be overwhelming for some users.
4. **Hypothetical Nature:** As a conceptual product, real-world performance may vary.
### Ideal User Profile
BrainScope is best suited for neurosurgical centers that are committed to providing the highest level of care and are willing to invest in advanced technology. It is particularly beneficial for centers that perform a high volume of complex craniectomy and craniotomy procedures. The system is also ideal for research institutions that are interested in using data-driven approaches to improve surgical outcomes.
### Key Alternatives (Briefly)
* **Traditional ICP Monitoring:** While effective, traditional ICP monitoring techniques provide less comprehensive data and lack the predictive capabilities of BrainScope.
* **Intraoperative MRI:** Intraoperative MRI provides high-resolution imaging but is more expensive and time-consuming than BrainScope.
### Expert Overall Verdict & Recommendation
BrainScope represents a significant advancement in neurosurgical technology. Its comprehensive monitoring capabilities, proactive intervention features, and enhanced surgical precision make it a valuable tool for improving patient outcomes. While the initial investment may be substantial, the long-term benefits of reduced complications and improved surgical success rates make BrainScope a worthwhile investment for neurosurgical centers. We highly recommend BrainScope for centers that are committed to providing the highest level of care and are willing to embrace innovative technology.
## Insightful Q&A Section
Here are 10 insightful questions that address genuine user pain points and advanced queries related to craniectomy vs craniotomy.
**Q1: What are the long-term cognitive effects of having a craniectomy compared to a craniotomy?**
*A: Both procedures can have potential cognitive effects, but the extent can vary. Craniectomy, due to the longer period without the bone flap, might initially lead to more noticeable effects related to brain protection and CSF dynamics. However, long-term cognitive outcomes depend heavily on the underlying condition being treated, the extent of brain damage, and rehabilitation efforts. Close monitoring and cognitive rehabilitation are essential in both cases.*
**Q2: How does the recovery process differ between a craniectomy and a craniotomy, and what can patients expect in terms of rehabilitation?**
*A: Recovery from a craniectomy generally involves a longer initial phase due to the need for the brain to adapt without the skull bone protection. Patients may experience visible scalp changes and require protective headgear. Craniotomy recovery might be slightly faster initially, but both procedures require comprehensive rehabilitation, including physical therapy, occupational therapy, and speech therapy, depending on the affected brain areas.*
**Q3: What are the risks associated with storing the bone flap after a craniectomy, and how are these risks mitigated?**
*A: Storing the bone flap carries risks of infection, resorption (bone breakdown), and contamination. To mitigate these risks, the bone flap is typically stored in a sterile environment, either frozen or in the patient’s abdomen. Antibiotics are administered to prevent infection, and the bone flap is carefully inspected before reimplantation.*
**Q4: How is the decision made between using the patient’s own bone flap versus a synthetic material during a cranioplasty after a craniectomy?**
*A: The decision depends on several factors, including the condition of the original bone flap, the size of the defect, and patient-specific considerations. If the original bone flap is healthy and intact, it is generally preferred. However, if it is infected or resorbed, synthetic materials like titanium mesh or custom-made implants may be used. Synthetic materials offer the advantage of being readily available and customizable.*
**Q5: What are the latest advancements in techniques for performing craniotomies and craniectomies that minimize brain damage?**
*A: Advancements include minimally invasive techniques using smaller incisions and endoscopic approaches, image-guided surgery with real-time navigation, and intraoperative monitoring to protect critical brain functions. These techniques aim to reduce the extent of brain retraction and minimize damage to surrounding tissues.*
**Q6: Are there any non-surgical alternatives to craniectomy or craniotomy for managing intracranial pressure?**
*A: Non-surgical options for managing intracranial pressure include medical management with medications like mannitol and hypertonic saline to reduce brain swelling, as well as interventions like CSF drainage via lumbar puncture or external ventricular drain (EVD). However, these measures are often temporary and may not be sufficient in severe cases requiring surgical decompression.*
**Q7: What are the potential complications associated with cranioplasty after a craniectomy, and how are they managed?**
*A: Potential complications of cranioplasty include infection, hematoma, bone flap resorption, and wound dehiscence. These complications are managed with antibiotics, drainage of hematomas, revision surgery, and careful wound care. Preoperative planning and meticulous surgical technique are crucial for minimizing these risks.*
**Q8: How do the costs of craniectomy and craniotomy compare, considering the need for a subsequent cranioplasty in craniectomy cases?**
*A: Craniectomy, with the subsequent cranioplasty, generally has higher overall costs compared to craniotomy due to the need for two separate surgical procedures, additional hospital stay, and potential complications associated with bone flap storage and reimplantation. However, the specific costs can vary depending on the hospital, surgeon fees, and insurance coverage.*
**Q9: What is the role of telemedicine in post-operative care for patients who have undergone craniectomy or craniotomy?**
*A: Telemedicine can play a significant role in post-operative care by facilitating remote monitoring of patients, providing virtual consultations, and addressing patient concerns from the comfort of their homes. This can improve access to care, reduce the need for frequent in-person visits, and enhance patient satisfaction.*
**Q10: What research is currently being conducted to improve outcomes for patients undergoing craniectomy and craniotomy procedures?**
*A: Research is focused on developing new techniques for minimizing brain damage during surgery, improving methods for managing intracranial pressure, optimizing bone flap storage and reimplantation, and enhancing post-operative rehabilitation. Clinical trials are also exploring the use of novel therapies to promote brain recovery and reduce long-term complications.*
## Conclusion & Strategic Call to Action
In summary, understanding the nuances of craniectomy vs craniotomy is essential for anyone involved in neurosurgical care. While both procedures involve accessing the brain, they differ significantly in their approach and purpose. Craniectomy is primarily used to relieve intracranial pressure by removing a portion of the skull, while craniotomy involves creating a temporary opening to access the brain for various procedures. BrainScope (hypothetically), or similar advanced neuro-monitoring systems, represents the future of neurosurgery, offering enhanced precision, proactive intervention, and improved patient outcomes.
As we look to the future, ongoing research and technological advancements promise to further refine these procedures and improve outcomes for patients with neurological conditions. The information provided here is intended to empower you with knowledge and understanding, but it is not a substitute for professional medical advice. Always consult with a qualified healthcare provider for diagnosis and treatment.
Now, we encourage you to delve deeper into this topic. Share your thoughts and experiences with craniectomy vs craniotomy in the comments section below. If you want to explore similar procedures, read our advanced guide to minimally invasive neurosurgery. Contact our experts for a personalized consultation on craniectomy vs craniotomy, and let us help you navigate the complexities of neurosurgical care.
